What Is The Most Effective Strategy For Inferior Calcaneal Spur

Overview
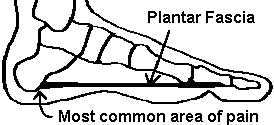
Heel spurs are a condition that usually makes its presence known first thing in the morning via heel pain. Discomfort is typically felt in the front and bottom of the heel (calcaneal). Pain can be constant for several months or intermittent for lengthy periods of time.
Causes
A bone spur forms as the body tries to repair itself by building extra bone. It generally forms in response to pressure, rubbing, or stress that continues over a long period of time. Some bone spurs form as part of the aging process. As we age, the slippery tissue called cartilage that covers the ends of the bones within joints breaks down and eventually wears away (osteoarthritis). Bone spurs due to aging are especially common in the joints of the spine and feet.
Symptoms
The vast majority of people who have heel spurs feel the asscociated pain during their first steps in the morning. The pain is quite intense and felt either the bottom or front of the heel bone. Typically, the sharp pain diminishes after being up for a while but continues as a dull ache. The pain characteristically returns when first standing up after sitting for long periods.
Diagnosis
Heel spurs and plantar fasciitis is usually diagnosed by your physiotherapist or sports doctor based on your symptoms, history and clinical examination. After confirming your heel spur or plantar fasciitis they will investigate WHY you are likely to be predisposed to heel spurs and develop a treatment plan to decrease your chance of future bouts. X-rays will show calcification or bone within the plantar fascia or at its insertion into the calcaneus. This is known as a calcaneal or heel spur. Ultrasound scans and MRI are used to identify any plantar fasciitis tears, inflammation or calcification. Pathology tests may identify spondyloarthritis, which can cause symptoms similar to plantar fasciitis.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are various ways to treat heel spurs. The first is to rest and apply ice to the afflicted area. Shoe inserts and night splints can also treat plantar fasciitis, and in turn, heels spurs. Unless you have stomach sensitivities, you may want to consider taking over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medication such as naprosyn to lower the swelling. A physical therapist can recommend gentle exercises and stretches to relax the tissue around the heel bone to relieve the tension. Even with these treatments, a stubborn heel spur may not go away. A physical therapist may decide to inject cortisone into the area to decrease inflammation, but that can cause other problems such as plantar fascial rupture and fat pad atrophy. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy is also an option, which uses energy pulses to apply microtrauma around the heel spur. Surgery is also an option but is not suggested unless the heel spur lasts more than a year. To prevent heel spurs from returning, shoe inserts can relieve the pressure on the plantar fascia. Also continue the recommended stretches and exercises.
Surgical Treatment
Heel spur surgery should only be considered after less invasive treatment methods have been explored and ruled insufficient. The traditional surgical approach to treating heel spurs requires a scalpel cut to the bottom of the food which allows the surgeon to access the bone spur. Endoscopic plantar fasciotomies (EPF) involve one or two small incisions in the foot which allow the surgeon to access and operate on the bone spur endoscopically. Taking a surgical approach to heel spur treatment is a topic to explore with a foot and ankle specialist.